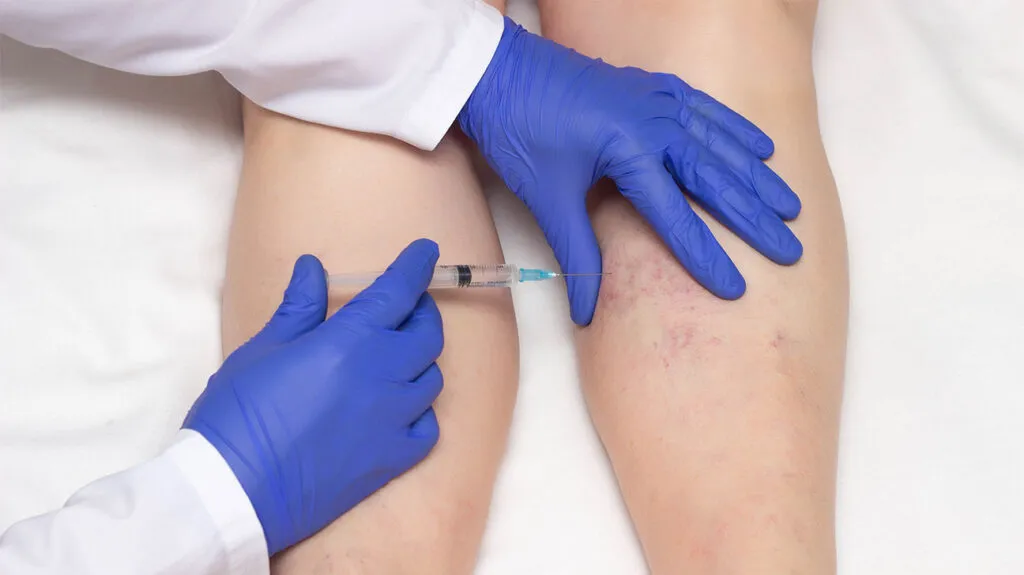
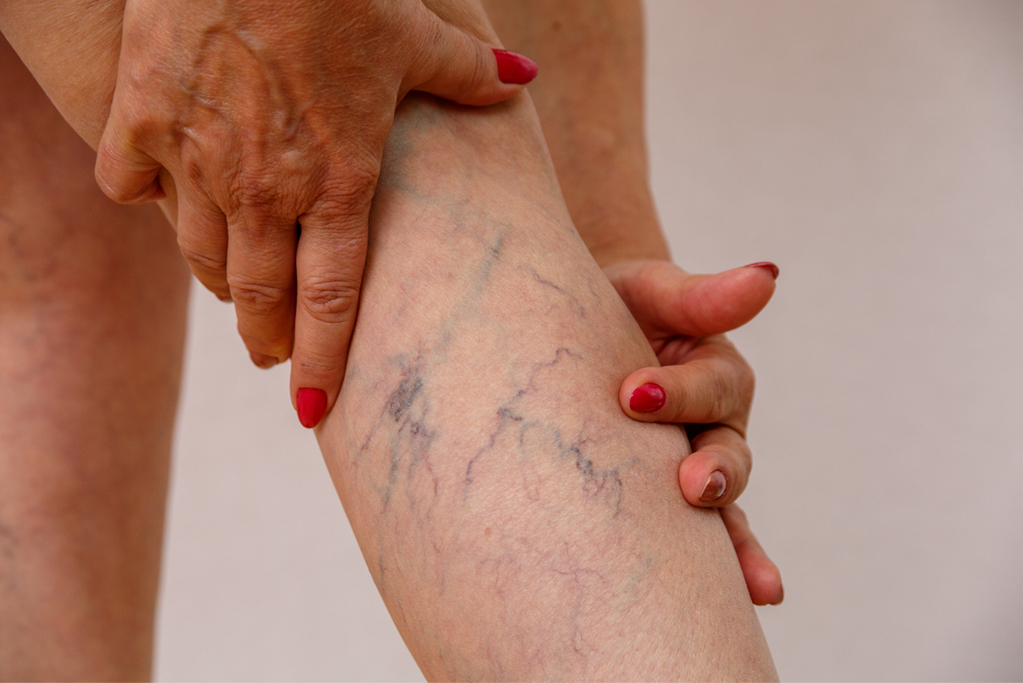
Capillary dilation(spider veins)
What is capillary dilation?
Capillary dilation, also known as telangiectasia or spider veins, refers to the enlargement of small veins on the surface of the skin. It commonly occurs in areas such as the legs, face, upper extremities, and chest wall. Most cases of capillary dilation do not present significant discomfort but rather pose cosmetic concerns. Consequently, it can be a source of distress, particularly for women, as it may impact their self-confidence and lifestyle to some extent.
What conditions can cause capillary dilation?
Congenital factors
Frequent exposure to sunlight
Pregnancy
Intake of vasodilating medications
Excessive alcohol consumption
Skin trauma
Surgical incisions
Acne Long-term oral or topical steroid use
Elderly individuals, as they have decreased vascular elasticity, making them more prone to capillary dilation
In addition, hormonal changes during menopause, use of hormonal contraceptives, and certain diseases such as ataxia telangiectasia, Bloom syndrome, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome, rhinophyma, spider angiomas, xeroderma pigmentosum, certain liver conditions, connective tissue disorders, lupus, and scleroderma, can also cause capillary dilation.
The majority of cases of capillary dilation have no specific cause and are simply a result of fair skin, aging, or hormonal changes. However, a small portion of capillary dilation may be caused by underlying medical conditions.
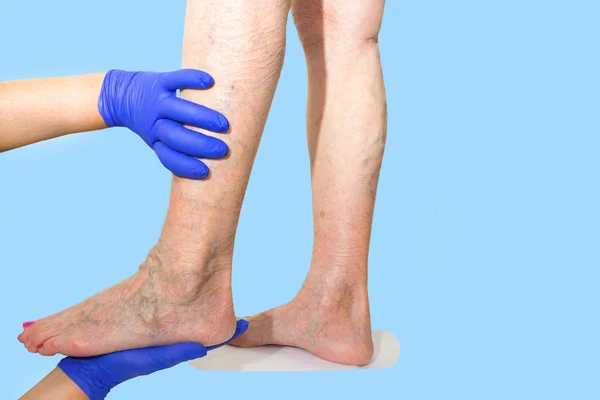
What are the symptoms of capillary dilation?
Most cases of capillary dilation do not present any symptoms. However, in some instances, bleeding may occur, which can have serious consequences if it happens in the brain or spinal cord.
Capillary dilation in the lower extremities may be an early sign of venous insufficiency. Research has shown that patients with capillary dilation in the lower limbs are more likely to have incompetent perforator veins, which means they are more prone to developing varicose veins. The likelihood of capillary dilation is also higher in obese individuals [1].
A small portion of individuals may experience localized itching and discomfort. Facial capillary dilation can lead to facial redness, affecting aesthetics and self-confidence.
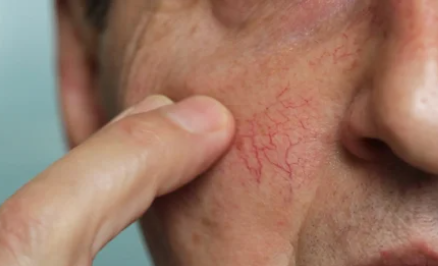
Are there any specific tests for capillary dilation?
Capillary dilation is quite common in individuals without any underlying health issues and is often a result of sun exposure or aging. However, individuals with severe systemic capillary dilation accompanied by significant vessel dilation should seek medical advice. If there is a family history of capillary dilation or if bleeding occurs in the oral or ocular regions, prompt medical assistance should be sought.
For capillary dilation in the lower extremities, it is advisable to visit a reputable hospital or specialized vein center. The doctor will conduct a detailed medical history inquiry, comprehensive physical examination, and accurate Doppler ultrasound assessment of the lower limb veins to determine if there are underlying venous insufficiency issues.
In addition, for certain conditions, blood tests, liver function tests, and imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
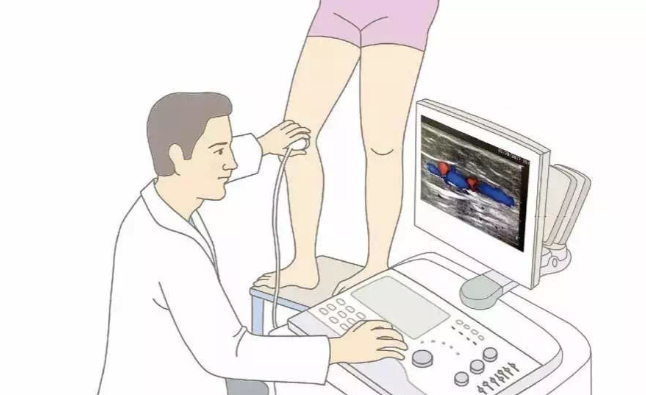
To alleviate symptoms of capillary dilation in the lower extremities, you can consider the following measures:
Avoid prolonged standing or sitting.
Avoid hot foot baths, as they can worsen capillary dilation.
Maintain a healthy weight and engage in weight control measures.
Avoid direct sunlight and use appropriate sun protection for exposed areas.
Avoid oral or topical steroid medications.
Limit alcohol consumption.
Treat any underlying related conditions.
If capillary dilation worsens rapidly or causes significant discomfort, it is advisable to seek medical advice.

The treatment of capillary dilation depends on individual circumstances and the presence of symptoms.
For most cases of capillary dilation that do not cause significant concerns, treatment may not be necessary. However, if capillary dilation is causing distress or affecting self-confidence, cosmetic treatments can be considered.
For individuals with symptomatic capillary dilation in the lower extremities, such as pain, swelling, or a heavy sensation, a Doppler ultrasound assessment of the lower limb veins should be performed before treatment to identify any superficial or deep venous insufficiency, as this may influence the treatment approach.
Currently, the main treatment methods for capillary dilation include sclerotherapy and laser therapy. Sclerotherapy is the preferred choice and can be combined with laser therapy for optimal results. Sclerotherapy is suitable for larger vessels with a diameter of more than 3mm, while laser therapy is appropriate for smaller vessels with a diameter of 3mm or less. The specific treatment approach may vary depending on individual differences and the preferences of the healthcare provider.